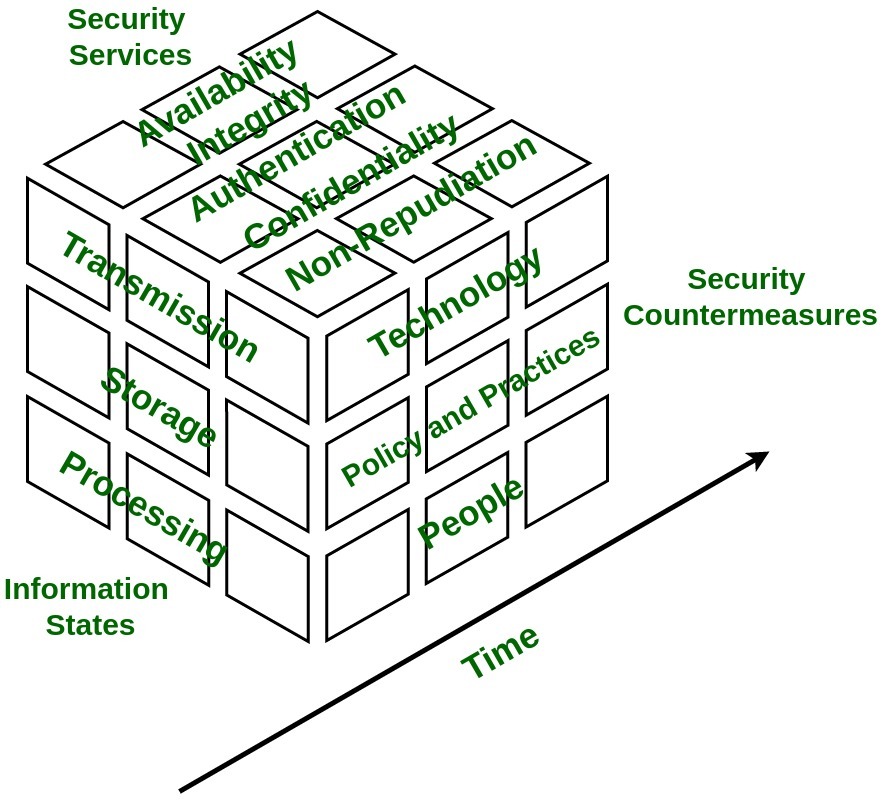
Information Assurance Model in Cyber Security
Information Assurance concerns implementation of methods that focused on protecting and safeguarding critical information and relevant information systems by assuring confidentiality, integrity, availability, and non-repudiation. It is strategic approach focused which focuses more on deployment of policies rather than building infrastructures.
Information Assurance Model :
The security model is multidimensional model based on four dimensions :
- Information States –
Information is referred to as interpretation of data which can be found in three states stored, processed, or transmitted.
- Security Services –
It is fundamental pillar of the model which provides security to system and consists of five services namely availability, integrity, confidentiality, authentication, and non-repudiation.
- Security Countermeasures –
This dimension has functionalities to save system from immediate vulnerability by accounting for technology, policy & practice, and people.
- Time –
This dimension can be viewed in many ways. At any given time data may be available offline or online, information and system might be in flux thus, introducing risk of unauthorized access. Therefore, in every phase of System Development Cycle, every aspect of Information Assurance model must be well defined and well implemented in order to minimize risk of unauthorized access.
Information States :
- Transmission –
It defines time wherein data is between processing steps. Example :
In transit over networks when user sends email to reader, including memory and storage encountered during delivery.
- Storage –
It defines time during which data is saved on medium such as hard drive.Example: Saving document on file server’s disk by user.
- Processing –
It defines time during which data is in processing state. Example :
Data is processed in random access memory (RAM) of workstation.
Security Services :
- Confidentiality–
It assures that information of system is not disclosed to unauthorized access and is read and interpreted only by persons authorized to do so. Protection of confidentiality prevents malicious access and accidental disclosure of information. Information that is considered to be confidential is called as sensitive information. To ensure confidentiality data is categorized into different categories according to damage severity and then accordingly strict measures are taken. Example :
Protecting email content to read by only desired set of users. This can be insured by data encryption. Two-factor authentication, strong passwords, security tokens, and biometric verification are some popular norms for authentication users to access sensitive data.
- Integrity –
It ensures that sensitive data is accurate and trustworthy and can not be created, changed, or deleted without proper authorization. Maintaining integrity involves modification or destruction of information by unauthorized access. To ensure integrity backups should be planned and implemented in order to restore any affected data in case of security breach. Besides this cryptographic checksum can also be used for verification of data. Example :
Implementation of measures to verify that e-mail content was not modified in transit. This can be achieved by using cryptography which will ensure that intended user receives correct and accurate information.
- Availability –
It guarantees reliable and constant access to sensitive data only by authorized users. It involves measures to sustain access to data in spite of system failures and sources of interference. To ensure availability of corrupted data must be eliminated, recovery time must be speed up and physical infrastructure must be improved. Example :
Accessing and throughput of e-mail service.
- Authentication –
It is security service that is designed to establish validity of transmission of message by verification of individual’s identity to receive specific category of information. To ensure availability of various single factors and multi-factor authentication methods are used. A single factor authentication method uses single parameter to verify users’ identity whereas two-factor authentication uses multiple factors to verify user’s identity. Example :
Entering username and password when we log in to website is example of authentication. Entering correct login information lets website verify our identity and ensures that only we access sensitive information.
- Non-Repudiation –
It is mechanism to ensure sender or receiver cannot deny fact that they are part of data transmission. When sender sends data to receiver, it receives delivery confirmation. When receiver receives message it has all information attached within message regarding sender. Example :
A common example is sending SMS from one mobile phone to another. After message is received confirmation message is displayed that receiver has received message. In return, message received by receiver contains all information about sender.
Security Countermeasures :
- People –
People are heart of information system. Administrators and users of information systems must follow policies and practice for designing good system. They must be informed regularly regarding information system and ready to act appropriately to safeguard system.
- Policy & Practice –
Every organization has some set of rules defined in form of policies that must be followed by every individual working in organization. These policies must be practiced in order to properly handle sensitive information whenever system gets compromised.
- Technology –
Appropriate technology such as firewalls, routers, and intrusion detection must be used in order to defend system from vulnerabilities, threats. The technology used must facilitate quick response whenever information security gets compromised.


